Vitamin E
Natural Tocopherols from plant oils
is highly valued for its superior antioxidant effects in cosmetics and food, as well as its positive health benefits in nutritional supplements and its skin healing properties.

Our product range
All grades of Vitamin E from our product range are of natural origin and GMO-free. Different grades other than the listed ones are available on request.
| Tocopherol Concentrates |
Mixed Tocopherols |
Tocopherol Esters |
| D-α-Tocopherol 1200 |
| D-α-Tocopherol 1000 |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
| Mixed Tocopherols 90% |
| Mixed Tocopherols 70% |
| Mixed Tocopherols 50% |
| |
| |
| |
|
| D-α-Tocopheryl Acetate 1250 |
| D-α-Tocopheryl Acetate 1100 |
| D-α-Tocopheryl Acetate 1000 |
| D-α-Tocopheryl Acetate 500 Powder |
| Tocopheryl Succinate 1210 |
| |
|
Chemistry of Vitamin E
Natural Vitamin E is a mixture of 8 different isomers - 4 forms of Tocopherols and 4 forms of
Tocotrienols. Commonly, the term Vitamin E is used synonymously with Tocopherol, more precisely with D-α-Tocopherol, which has the highest biological activity. However, the 8 isomers in Vitamin E have different individual biological activity and deliver different therapeutic benefits. It is known that all 8 isomers of the Vitamin E family work synergistically in the human body.
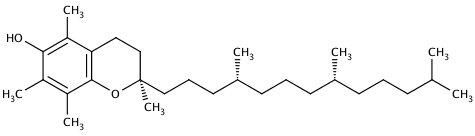
|
| D-α-Tocopherol |
Unlike the natural grade, synthetic Vitamin E is composed of the racemic form of the Tocopherols (D,L-α-Tocopherol). It exhibits a lower activity compared to natural Vitamin E and is therefore considered to be of inferior quality.
Besides the mixed Tocopherols and pure D-α-Tocopherol grades, the Acetate and Succinate Esters of D-α-Tocopherol have advantages that allow for flexibility in product formulations. Even though, the Esters do not have high antioxidant effect of the free Tocopherols, but they have reduced susceptibility to degradation when exposed to air or elevated processing temperatures and are more stable during storage.
The different types of Vitamin E
The first yield of extraction of natural Vitamin E from plant-source oil are the
Mixed Tocopherols, which are available in concentrations of 50%, 70% and 90%. It has been shown that the natural Tocopherol mixture consisting of D-α-, D-β-, D-γ- und D-δ-Tocopherol offers better protection from oxidation (rancidity) than pure D-α-Tocopherol (see
Tocopherols as Food Antioxidants). Generally, the 70% concentration of the Mixed Tocopherols is often used in foods and cosmetics.
Since only the D-α-form has a proven biological activity, many products are formulated with a high concentration of
D-α-Tocopherol. For the α-tocopherol form of Vitamin E, 1 mg equals about 1.49 IU. However, this form has not found many applications in cosmetic products due to its limited shelf life (indicating strong antioxidant activity). Frequently used D-α-Tocopherol concentrates contain concentration of about 65% to 80%.
The Vitamin E product range of oil concentrates is completed by the types that consist of the stable ester form
D-α-Tocopherol Acetate. This stable form is also commonly used in combination products, where the activity of Vitamin E may be suppressed by other substances in cosmetic formulations. Apart from skin conditioning effects and a sun protection factor of 2, it exhibits no antioxidant or free radical scavenging properties (as falsely claimed by many cosmetic products). In its esterified form, α-Tocopheryl Acetate has no antioxidant activity because the active phenol is blocked by esterification.
The oil based products are commonly used in capsules, liquid based nutritional supplement preparations and cosmetic formulations. The microencapsulated ester form D-α-Tocopherol Acetate and the powdered D-α-Tocopherol Succinate are commonly used in tablets and granules.
Links
The Vitamin E Factor
Tocopherols as Food Antioxidants




